How Do You Measure Up?
Reading time: 4 ½ minutes
If you're anything like me, when I read about physical strength, the competitive part of me wonders, 'how am I doing compared to others my age?' Because we have more than 650 muscles in our body and they all produce different movements, there is no single exercise which determines 'strength'. However, the following 4 exercises will help you identify areas of your body where you are strong and areas you may need to work on. Remember, the guidelines are supposed to be motivational. If you are not currently at the levels you would like to be, you now have a new goal! Having a measure of how we are doing allows us to assess our current habits and tweak our fitness / movement regime if we need to. Think of these tests as quick performance checks for your strength, balance, and power – the essential health components that help you stay active, independent, and doing what you love. As with all exercise, it’s important to be strict with your technique and don't do anything which could exacerbate a current injury.
Test 1: Squat to Chair Test
This test is a measure of lower body power. If you can perform a hip hinge correctly and you can get out of a chair without using your arms, then you're setting yourself up to age well. For this test, all you need to do is count how many times you can go from sitting to standing (without using your hands) in 30 seconds. Find a chair with a straight back and no armrests. Sit in the chair with your feet flat on the floor, and place your arms across your chest, resting your hands on your shoulders. Using a timer set for 30 seconds, stand up, then sit down and repeat. Count how many repetitions you can perform in the time available. Ensure you maintain good squat technique throughout. If you're unsure about your form, please see this video demonstration.
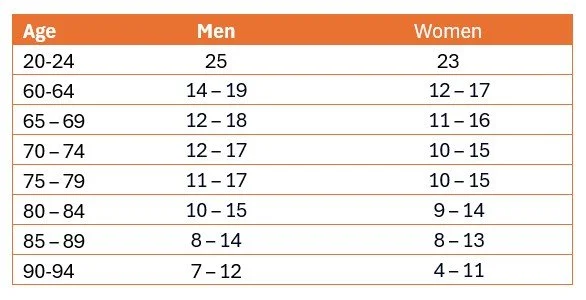
Benchmarks
These average scores do not take into account a person's medical history – for example if they have recently undergone surgery or have an injury.
As you will notice, the study referenced only used participants over the age of 60 years old, so there is no data between the ages of 26-59. However, if you are in the age band without any benchmark, we still feel this is a good test to assess how you are performing at present.
Here is a link to an interesting BBC article if you want to read further.
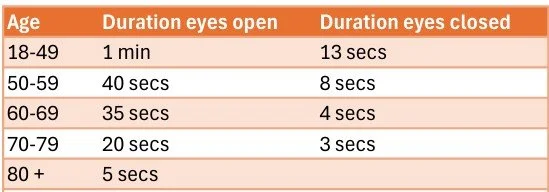
Test 2: Single Leg Balance Test (aka The Flamingo)
Holding this position is a great test of balance. In bare feet (or wearing suitable footwear), put your hands on your hips and lift one foot off the floor so you’re standing on one leg. Without leaning against anything or using your hands to steady yourself, see how long you can stay balanced before returning your raised foot to the ground. Take the best of three attempts and then repeat, with your eyes closed. This is tough and you may be surprised by how quickly you need to steady yourself! The NHS suggests the following targets:
The ‘Dead Hang’ is a test of grip, upper body strength and muscle mass. It requires us to engage muscles in the arms, abs, back and shoulders. It has recently come to scientists attention that grip strength is a better predictor for premature death than other more obvious indicators such as blood pressure so it is vital we don't neglect it in our training. To try this test you might need to head out to the monkey bars at your local park (unless you have a sturdy pull-up bar at home). Grip the bar overhead with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width. Engage your core, then bend at the knees to lift your feet off the floor. Hold for as long as you can. Whilst this exercise looks a bit arbitrary, it is a good measure of overall strength so getting a good result means it is more likely you'll be able to carry children, grandchildren, lift suitcases and push lawnmowers. Below are guidelines about the length of time we should be aiming to hold this position:
20s & 30s: Target: 60-90 seconds hold
40s & 50s: Target: 20-45 seconds hold
60s & 70s: Target: 10-15 seconds hold
Karen tried this for fun in November last year (pictured) and managed to hold for 39 seconds. She tried it again after completing our 6 Week Online Body Transformation Programme (which increased her upper body strength by 52%) and she held for 60 seconds.
Test 4: Sitting Rising Test
This is one of the trickier tests, so do take care and use common sense (i.e. do not perform if you currently have knee, hip or back issues).
Start with no shoes on. Cross your legs and try to lower yourself to the ground without putting your hands or knees down. Once on the floor in a seated position, try to stand up again without using any other part of your body to help. We score this test by starting out with 10 points. We lose a point every time a hand or knee is used. If you wobble, you lose half a point. Angela Rippon explains it well in this article. 8-10 points is a great score and what we are ultimately looking to achieve. If you are not currently at this level, full body strengthening exercises, stretches for hip flexibility and exercises which challenge your balance will help you improve and enable you to score more points.
To sum up:
Give these 4 exercises a try if you'd like to see how your strength levels are, compared to where we would like them to be. Remember, as we said above, the guidelines are supposed to be motivational. It may mean that you add some strengthening exercises in to your weekly routine so you can improve your scores. One thing is for sure however, we neglect strength at our peril. If we want to stay active, independent, and doing what we love, it is a vital part of fitness to maintain!